What is Thrush?
Thrush, also known as candidiasis, is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of the yeast species Candida. It can affect various parts of the body, including the mouth, throat, and genital area. Thrush is most commonly seen in women, but it can affect anyone, including men and babies. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options for thrush, as well as natural remedies and preventive measures.
Causes of Thrush
Thrush is caused by an overgrowth of the yeast Candida, which normally lives in small amounts in the mouth, digestive tract, and vaginal area. However, when the body's natural balance is disrupted, the yeast can multiply rapidly, leading to an infection. Several factors can trigger this overgrowth, including:
- Antibiotic use: Antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body, allowing Candida to thrive.
- Weakened immune system: Conditions such as HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or the use of immunosuppressive medications can make individuals more susceptible to thrush.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone replacement therapy can alter the balance of yeast in the body, making thrush more likely.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels provide an ideal environment for Candida to grow, especially if diabetes is not well controlled.
- Poor oral hygiene: Not brushing your teeth regularly can lead to a buildup of bacteria and yeast in the mouth, increasing the risk of oral thrush.
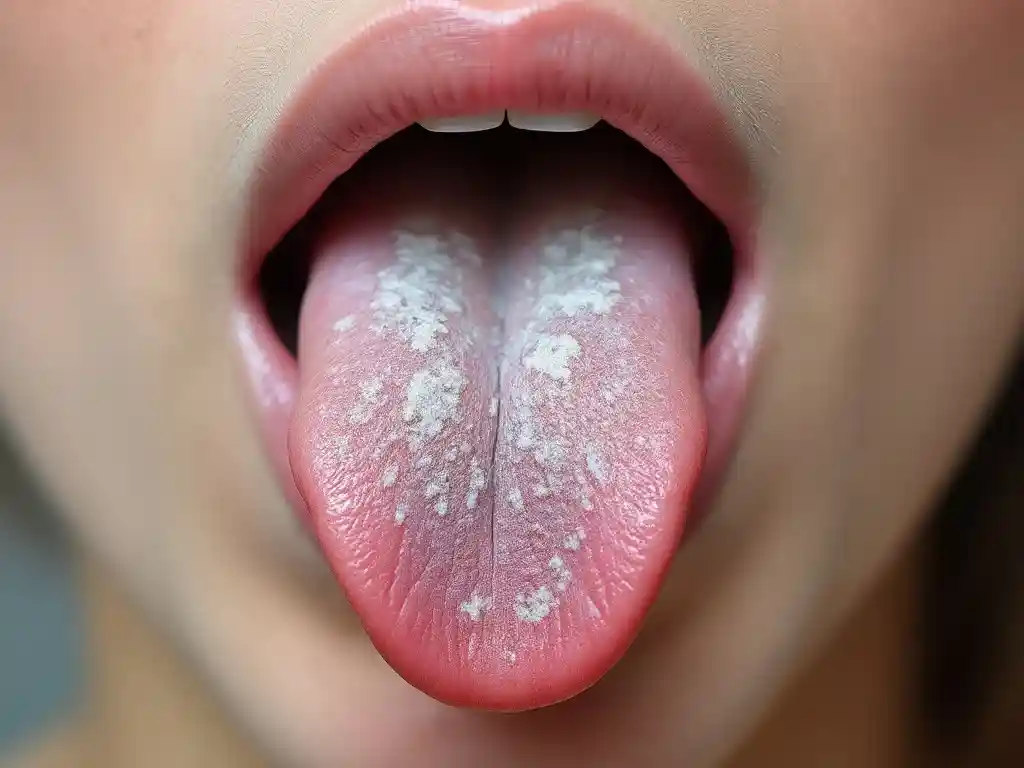
Symptoms of Thrush
The symptoms of thrush vary depending on the area of the body affected. Common symptoms include:
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush is one of the most common forms of thrush, and it can cause symptoms such as:
- White, creamy lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, or roof of the mouth
- Redness or soreness in the affected areas
- Pain or difficulty swallowing
- Loss of taste or a cotton-like feeling in the mouth
Oral thrush is more common in infants, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Vaginal Thrush
Vaginal thrush is another common form of the infection, which causes symptoms such as:
- Itching, irritation, and redness around the vagina
- Thick, white discharge that resembles cottage cheese
- Pain or discomfort during intercourse
- Painful urination
Vaginal thrush can be triggered by antibiotics, pregnancy, or hormonal changes.
Invasive Thrush
In some cases, the infection can become invasive, affecting internal organs. This is more common in people with weakened immune systems. Symptoms of invasive thrush may include:
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue and weakness
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain (if the infection affects the lungs)
If left untreated, invasive thrush can be life-threatening.
How Thrush is Diagnosed
Thrush is typically diagnosed based on the symptoms and a physical examination. In some cases, a sample of the affected tissue may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of Candida. For vaginal thrush, a swab of the vaginal discharge may be tested in a laboratory. If the infection is recurrent or severe, further testing may be done to check for underlying conditions such as diabetes or immune system disorders.
Treatment Options for Thrush
Thrush is usually treated with antifungal medications, which can be administered in different forms, including creams, oral tablets, or lozenges. The choice of treatment depends on the type of thrush and the severity of the infection:
- Oral Thrush: Treatment often involves antifungal medications such as nystatin, fluconazole, or clotrimazole. These can be taken as oral tablets, lozenges, or mouth rinses.
- Vaginal Thrush: Antifungal creams, tablets, or suppositories such as clotrimazole, miconazole, or fluconazole are commonly used to treat vaginal thrush.
- Invasive Thrush: In severe cases, antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B or caspofungin may be required, especially if the infection has spread to the bloodstream or internal organs.
In most cases, thrush responds well to antifungal treatment, but it is essential to complete the full course of medication to ensure the infection is fully cleared.
Natural Remedies for Thrush
In addition to conventional treatments, several natural remedies may help manage and prevent thrush:
- Probiotics: Probiotics, particularly those containing Lactobacillus acidophilus, can help restore the balance of healthy bacteria in the gut and reduce the overgrowth of Candida.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, tea tree oil can be diluted and applied topically to the affected area (such as the vagina or mouth) to help fight the infection.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil has natural antifungal properties and can be used to treat skin and vaginal thrush by applying it directly to the affected area.
- Garlic: Garlic is renowned for its antibacterial and antifungal properties. It can be included in the diet or applied topically to help combat fungal infections.
Prevention of Thrush
To prevent thrush, consider the following tips:
- Maintain good oral hygiene, brushing and flossing your teeth regularly to prevent oral thrush.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing and cotton underwear to prevent vaginal thrush.
- Control blood sugar levels if you have diabetes, as high blood sugar can promote the growth of Candida.
- Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics, as they can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the body.
Conclusion
Thrush is a common fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body. While it is typically easy to treat with antifungal medications, it is essential to address the underlying causes and take steps to prevent recurrence. If you suspect you have thrush, it is important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. By maintaining good hygiene and making lifestyle changes, you can reduce the risk of developing thrush.
