Understanding Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition characterized by pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back through the hips and down each leg. Sciatica is not a diagnosis but a symptom of an underlying issue, often a herniated disk, spinal stenosis, or degenerative disc disease. The pain associated with sciatica can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the affected leg. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for sciatica can help manage pain and improve quality of life.
Causes of Sciatica
Sciatica results from irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, usually due to a spinal issue. Common causes include:
- Herniated Disc: A herniated or slipped disc in the spine can press on the sciatic nerve, causing pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal can compress the nerves, leading to sciatica.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related wear on the spine can lead to sciatica by reducing disc cushioning and causing nerve compression.
- Bone Spurs: Bone growths along the spine can pinch the sciatic nerve, triggering pain.
- Injury: Trauma to the lower back or hips can lead to nerve irritation and sciatica.
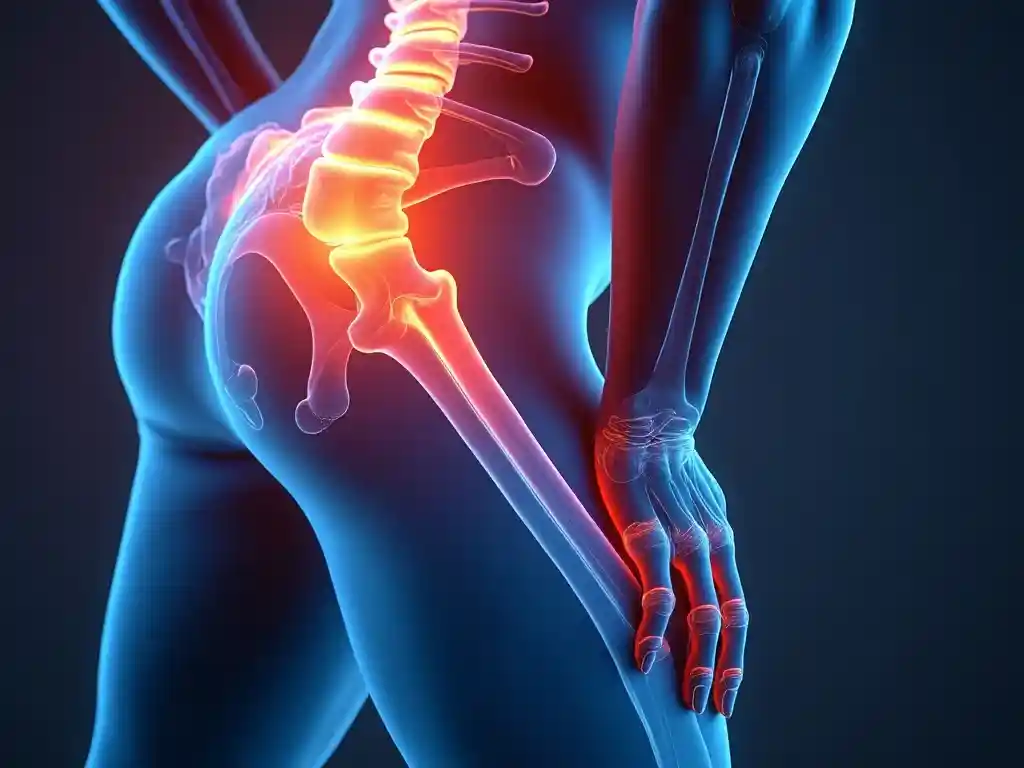
Symptoms of Sciatica
The hallmark symptom of sciatica is pain that radiates from the lower back down to the buttock and back of the leg. Sciatica symptoms may vary but commonly include:
- Sharp, Shooting Pain: The pain often radiates down the leg and can feel like a jolt or electric shock.
- Numbness and Tingling: Many people with sciatica experience numbness or tingling in the leg or foot.
- Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness may occur in the leg or foot, making it challenging to move or stand.
- Pain Worsening with Movement: Activities like bending, twisting, or prolonged sitting can worsen the pain.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Sciatica
Diagnosing sciatica typically involves a physical examination and a review of symptoms. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are used to identify the underlying cause of the nerve compression.
Treatment for sciatica focuses on pain relief, reducing inflammation, and addressing the root cause of the nerve compression. Common treatments include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises and stretches can relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve, improve mobility, and strengthen the core and back muscles.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and, in severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Cold and Heat Therapy: Alternating cold and heat packs can reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments may help realign the spine, reducing pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary to relieve nerve pressure.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Tips for Managing Sciatica
In addition to conventional treatments, several lifestyle changes and natural remedies may support sciatica relief and promote overall spine health:
- Regular Stretching: Gentle stretches targeting the lower back, hamstrings, and piriformis muscles can relieve tension on the sciatic nerve.
- Exercise Regularly: Low-impact exercises, such as walking, swimming, and yoga, can strengthen the back and core muscles, reducing sciatic nerve pressure.
- Maintain Good Posture: Proper posture when sitting, standing, and sleeping can help reduce strain on the lower back and prevent sciatic pain.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the lower back, preventing nerve compression.
- Massage Therapy: Massage may help relieve muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain associated with sciatica.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs, such as turmeric and devil's claw, have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce pain and inflammation. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting herbal supplements.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can help manage pain and reduce stress, which can exacerbate sciatica symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience severe pain, sudden weakness, or numbness in the leg, or if you have difficulty controlling bladder or bowel functions, seek medical attention immediately. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition requiring prompt treatment. For most cases of sciatica, early diagnosis and intervention can prevent symptoms from worsening and reduce the need for surgery.
Conclusion
Sciatica is a common condition that can significantly impact daily life, but with the right combination of treatments, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies, many people can manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Understanding the causes and symptoms of sciatica is the first step in seeking effective treatment. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, engaging in regular physical activity, and practicing good posture can help prevent future flare-ups and support long-term spine health.
