Understanding Herpes
Herpes is a common viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). The two main types of HSV are HSV-1 and HSV-2. HSV-1 primarily causes oral herpes, leading to cold sores around the mouth, while HSV-2 is typically associated with genital herpes, causing sores in the genital and anal areas. Although there is no cure for herpes, effective treatments are available to manage outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmission.
Causes and Risk Factors of Herpes
Herpes is caused by the herpes simplex virus, which can be transmitted through close contact with an infected person. The virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate later in life, causing outbreaks. The two types of herpes simplex virus are:
- HSV-1 (Oral Herpes): Typically causes cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth, but it can also cause genital herpes through oral-genital contact.
- HSV-2 (Genital Herpes): Generally causes painful sores in the genital and anal regions, but can also affect the mouth through oral sex.
Risk factors for contracting herpes include:
- Unprotected Sexual Contact: The most common way HSV-2 is transmitted is through sexual contact with an infected person.
- Close Physical Contact: HSV-1 can be spread through kissing or sharing utensils, towels, or razors with someone who has an active outbreak.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with HIV/AIDS or those on immunosuppressive medications, are more susceptible to herpes outbreaks.
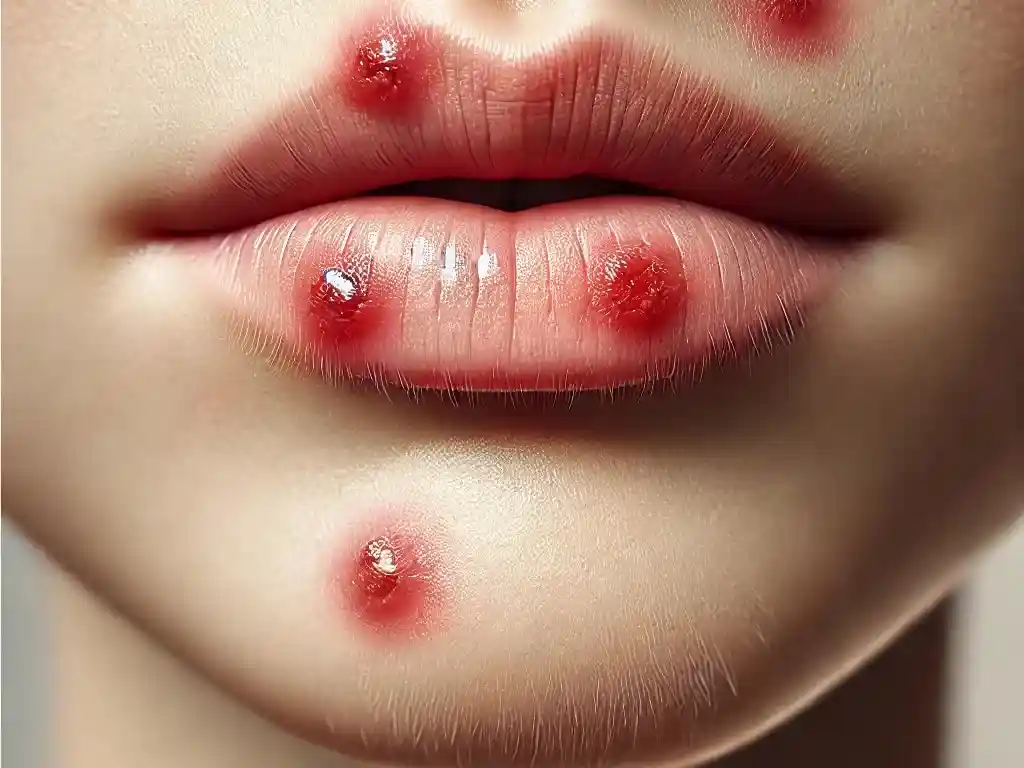
Symptoms of Herpes
Herpes symptoms vary depending on the type of virus and whether the infection is primary or recurrent. Some people with herpes may never experience symptoms, while others may have frequent outbreaks. Common symptoms include:
- Oral Herpes (HSV-1): Painful cold sores or blisters around the mouth or lips. Initial symptoms may include itching, burning, or tingling before sores appear.
- Genital Herpes (HSV-2): Painful blisters or sores in the genital area, itching, burning sensation while urinating, and flu-like symptoms (fever, body aches).
- Recurrent Outbreaks: After the initial infection, the virus remains dormant in the body. Stress, illness, or weakened immunity can trigger recurrent outbreaks, which are usually less severe than the first outbreak.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Herpes
Herpes is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and, in some cases, laboratory tests. If sores are present, a doctor may take a sample from the sores and test it for the presence of the herpes virus. Blood tests can also detect HSV antibodies, indicating a previous infection.
While there is no cure for herpes, treatments can help manage outbreaks and reduce symptoms. Common treatments include:
- Antiviral Medications: Medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir can help reduce the severity and duration of herpes outbreaks. These drugs work by inhibiting the replication of the herpes virus in the body.
- Topical Creams: Over-the-counter creams like docosanol (Abreva) can help relieve symptoms of oral herpes, such as itching and burning.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage the discomfort associated with herpes outbreaks.
- Supplements: Some studies suggest that certain supplements, such as lysine, may help reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks, although more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
Natural Remedies for Herpes
In addition to conventional treatments, several natural remedies may help alleviate symptoms and support recovery from herpes outbreaks. Some of these remedies include:
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera has antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties. Applying aloe vera gel to the affected area may help soothe sores and reduce swelling and irritation.
- Honey: Honey, especially manuka honey, has natural antiviral and healing properties. Applying honey to sores may promote healing and prevent secondary bacterial infections.
- Essential Oils: Essential oils such as tea tree oil, lemon balm, and peppermint oil may help reduce inflammation and soothe painful sores. However, essential oils should always be diluted with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation.
- CBD (Cannabidiol): CBD oil may help reduce pain and inflammation associated with herpes outbreaks. Some users report that applying CBD topically or taking it orally can provide relief from itching and discomfort during an outbreak. Consult with a healthcare provider before using CBD, especially if you are on other medications.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C supports the immune system, which is important for managing herpes outbreaks. Foods rich in vitamin C, such as oranges, strawberries, and bell peppers, may help strengthen the body’s defenses against the virus.
- Licorice Root: Licorice root contains glycyrrhizin, which may have antiviral properties. Topical applications of licorice root extract may help speed up healing and alleviate symptoms of herpes sores.
Preventing Herpes Outbreaks
Although herpes is highly contagious, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others and prevent future outbreaks:
- Use Protection: Condoms or dental dams can reduce the risk of transmitting genital herpes during sexual activity, though they do not eliminate the risk completely.
- Avoiding Contact During Outbreaks: Avoid kissing or engaging in sexual activity during an outbreak, as this is when the virus is most contagious.
- Boost Your Immune System: A healthy immune system can help keep herpes outbreaks in check. Eating a balanced diet, managing stress, and getting regular exercise can help support your immunity.
- Reduce Triggers: Stress, illness, and hormonal changes can trigger herpes outbreaks. Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing may help reduce the frequency of outbreaks.
Conclusion
Herpes is a common viral infection that can affect both the mouth and genital areas. While there is no cure, antiviral medications and natural remedies can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of outbreaks. Maintaining a healthy immune system and avoiding triggers are key to preventing outbreaks. If you suspect you have herpes or are experiencing symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider to receive appropriate treatment and guidance.
